The Advancing Role of Artificial Intelligence in the Logistics Sector
After the widespread disruption of COVID-19 and other impacts, supply chains are big news. It’s no surprise: every product you have in your possession has passed through a supply chain. Like most industries in today’s world, this sector is being impacted by the advancement of technologies such as artificial intelligence (AI).
To understand its implications, let’s first define what a supply chain is: the network that moves a product through production, vendors, warehouses, transport, distribution centers, and retailers until it reaches the end consumer.1 For most logistics companies, the supply chain can be riddled with inefficiencies and wastage, some of which have been exacerbated by the COVID-19 pandemic:
- Poor or limited planning capability that results in mismatched supply and demand, and difficulties in managing inventory costs and sales and operations planning2
- Full warehouses with inventory that doesn’t match up with baseline demand3
- Weak infrastructure and conflicts of interest causing delays4
- Issues with integrating B2B solutions stemming from old legacy applications, too many manual processes, and too much custom code5
- Lack of transparency across the supply chain, meaning organizations can’t react to unanticipated risks or changing demand6
The solution? AI is being used to optimize supply chains around the world. The test of agility and resilience posed by the COVID-19 pandemic only accelerated the digitalization and modernization efforts over which executives had already been mulling. Companies worked to mitigate risk by investing in digital initiatives to increase visibility, reduce costs, automate processes, and glean analytical insights.7
Common supply chain problems and AI solutions
Increased demands from shippers have pushed organizations to explore intelligent technology. Some of the most common solutions that AI technology offers in the supply chain are:
- Identifying the possible impacts of supply disruptions, demand changes, or departures from what has been planned8
- Automating administrative tasks like filing paperwork, which frees employees up to focus on other projects9
- Forecasting customer demand through AI-driven data analytics, enabling more efficient warehouse management10
- Saving money through dynamic, fully automated should-cost models that respond to market changes in real time11
- Analyzing traffic and weather conditions to optimize routes, saving time, fuel, and money12
- Advanced image recognition that identifies the condition of products and manufacturing processes13
Efficiency and financial drivers for AI in logistics
Investment in advanced supply chain technology has increased in recent years, with the market for AI-related solutions expected to reach $16.7 billion by 2027.14
AI solutions can help identify exactly which steps in a supply chain can be improved in order to improve profits, manage carrier contracts, and even negotiate shipping and procurement rates.15 It can help reduce conversion costs (all manufacturing costs bar those of raw materials) by 20 percent, with higher workforce productivity accounting for up to 70 percent of the cost reduction.16 McKinsey found that early adopters who successfully implemented AI supply chain solutions reported a 15 percent reduction in logistics costs.17
Cognitive automation, which is similar to robotic process automation, but typically works with unstructured data, can be used to create self-driving supply chains. These systems could provide real-time recommendations, make predictions, and take decisions within the scope of predefined rules. This could increase efficiency, which means reduced costs.18
The framework below can serve as a guide to know what AI process could be implemented for cost reduction.
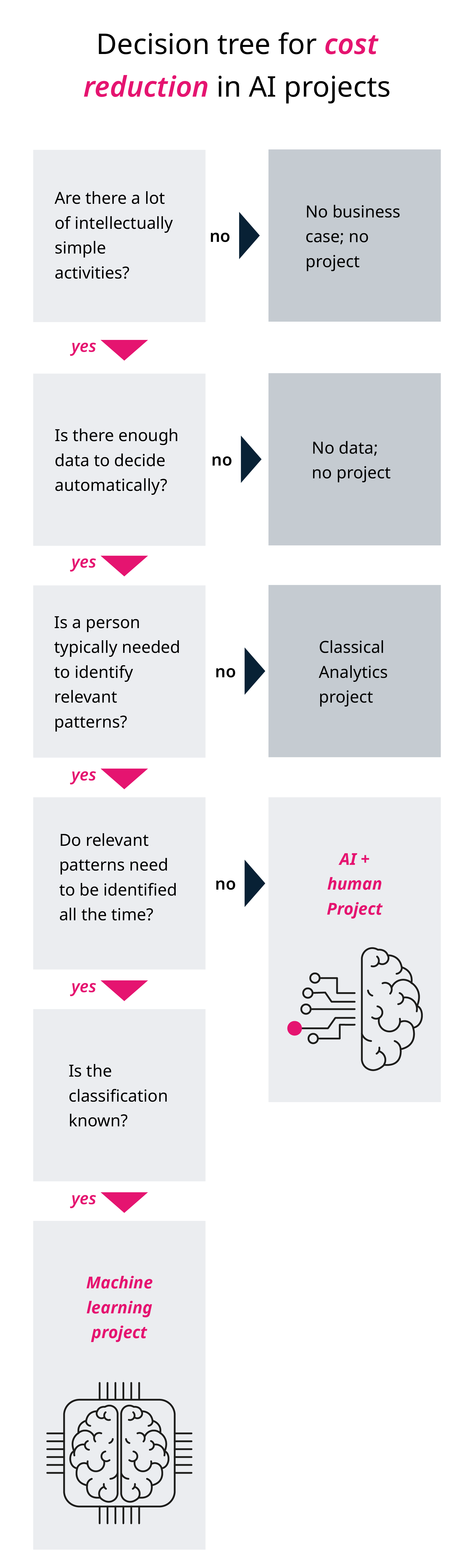
How AI is successfully being applied in supply chain management
Established organizations are already embracing and utilizing AI and machine learning (ML) to improve their supply chains in a number of ways.
Automated warehouses
Large corporations that have a need for fast and complex logistics solutions, such as Amazon, are investing their own resources to promote innovation in AI and robotics in order to facilitate automated warehousing. Amazon has been investing heavily in warehouse automation for a decade, acquiring companies, hiring top researchers, and funding challenges to find innovative solutions. However, the robots it has deployed so far display limited intelligence and can perform only basic tasks, demonstrating how far even a company with such immense resources still has to go.19
Another case in point is Ocado, an online-only supermarket in the UK. Their highly automated warehouses are optimizing logistics so effectively that other grocery chains are buying their AI-driven warehousing technology.20 Ocado’s automated factory employs 3,000 robots controlled by an AI traffic controller. The robots move on a grid containing 21 stacked containers of merchandise, ordered by frequency of use to expedite the picking process. Multiple robots work together to lift crates until the right one is found, whereupon one robot delivers the items to a shelf to be packed by a human. Ocado says its goal is to automate the process completely, from receiving orders to delivery.21
Route optimization
Global shipping and logistics company UPS employs a system called On-Road Integrated Optimization and Navigation (ORION), which it says originally reduced driver miles by an average of eight per day. The company recently upgraded the system with dynamic routing, which evaluates changing conditions constantly and feeds optimized route information to drivers, saving a further two-to-four miles on average.22 Crucially, UPS estimates that every daily driver mile saved can add up to $50 million in savings per year.23
Predictive maintenance
Utilizing past and present data, ML algorithms can make predictions and recommendations about vehicle maintenance, increasing fleet lifespan and reducing downtime. Technology company Uptake combines AI and ML to analyze data from Internet of Things devices, GPS, and vehicle logs to predict mechanical failures for vehicles including trucks, planes, and railcars.24
How AI optimizes inventory management
Effective management of inventory is paramount to customer satisfaction and competitive advantage.25 AI can improve inventory management in the following ways:
- Spotting defective products or packaging to prevent customers from receiving faulty items and reduce returns26
- Increasing visibility through a unified, AI-powered inventory and warehouse management system that automates replenishments and adjusts the supply network using predictive inventory alerts can reduce operational costs and prevent out-of-stock issues27
- Evaluating factors such as seasonal trends, marketplace environment, sales, promotions, and other historical data to predict demand and prevent under- or overstocking28
- Automating materials procurement through vendor matching, classifying spending, collecting supplier and market data, and detecting anomalies29
The logistics sector is complex and multilayered, requiring the ability to plan, be resilient, and be flexible. However, with the right platform, automation of logistical work processes can enable production operations to be decentralized to cheaper areas, improve customer satisfaction, control costs, and reduce staff requirements.30 Going forward, businesses that incorporate AI into their supply chains stand the chance to gain a critical advantage in an increasingly competitive environment.
Turn disruptive technology to your advantage with a range of online courses
- 1 Kenton, W. (Aug, 2021). ‘Supply chain’. Retrieved from Investopedia.
- 2 Kroschl, C. (Sep, 2021). ‘The how and the why of inefficiencies in supply plans’. Retrieved from Camelot Consulting Group.
- 3 Cecere, L. (Nov, 2021). ‘Managing supply in the face of unprecedented inefficiency’. Retrieved from Forbes.
- 4 Cecere, L. (Nov, 2021). ‘Managing supply in the face of unprecedented inefficiency’. Retrieved from Forbes.
- 5 Barker, I. (Mar, 2022). ‘Poor integration and lack of supply chain agility costs businesses dear’. Retrieved from BetaNews.
- 6 Wilson, G. (May, 2021). ‘Realising end-to-end transparency in the supply chain’. Retrieved from Supply Chain Digital.
- 7 Stackpole, B. (Feb, 2021). ‘Fueled by new technologies, the future of supply chains is here’. Retrieved from TechTarget.
- 8 Simchi-Levi, D. & Timmermans, K. (Oct, 2021). ‘A simpler way to modernize your supply chain’. Retrieved from Harvard Business Review.
- 9 Nichols, M. (Jun, 2020). ‘10 Ways AI improves distribution and the supply chain’. Retrieved from Towards Data Science.
- 10 Nichols, M. (Jun, 2020). ‘10 Ways AI improves distribution and the supply chain’. Retrieved from Towards Data Science.
- 11 (Apr, 2021). ‘3 Ways artificial intelligence/AI can help with supply chain digital transformation’. Retrieved from SupplyChain247.
- 12 Nichols, M. (Jun, 2020). ‘10 Ways AI improves distribution and the supply chain’. Retrieved from Towards Data Science.
- 13 Owczarek, D. (Feb, 2021). ‘AI in supply chain management’. Retrieved from Nexocode.
- 14 (Feb, 2022). ‘Global AI in supply chain management market 2022-2027: Challenges, opportunities, ecosystem company analysis, case studies, recommendations’. Retrieved from GlobeNewswire.
- 15 Hunt, S. (Oct, 2021). ‘Artificial intelligence (AI) in supply chains’. Retrieved from Datamation.
- 16 Wilson, G. (May, 2020). ‘BCG: the future of factories with AI’. Retrieved from Supply Chain Digital.
- 17 Alicke, K., et al. (Apr, 2021). ‘Succeeding in the AI supply-chain revolution’. Retrieved from McKinsey.
- 18 Minevich, M. (Nov, 2021). ‘Can artificial intelligence save America from the global supply chain disaster?’. Retrieved from Forbes.
- 19 Knight, W. (Nov, 2021). ‘Robots won’t close the warehouse worker gap anytime soon’. Retrieved from Wired.
- 20 Browne, R. (Jan, 2022). ‘Ocado unveils lighter robots to help grocery giants like Kroger take on Amazon’. Retrieved from CNBC.
- 21 Davis, M. (Apr, 2021). ‘3,000 Robots working in Ocado’s automated warehouse for faster online grocery’. Retrieved from Science Times.
- 22 Leonard, M. (Jun, 2021). ‘UPS adds dynamic routing to ORION, saving 2-4 miles per driver’. Retrieved from Supply Chain Dive.
- 23 Hamilton, J. (Mar, 2021). ‘How AI is changing the future of supply chain costs’. Retrieved from Robotics Tomorrow.
- 24 Hunt, S. (Oct, 2021). ‘Artificial intelligence (AI) in supply chains’. Retrieved from Datamation.
- 25 Jenkins, A. (Apr, 2021). ‘14 Top inventory management trends to know in 2021’. Retrieved from Netsuite.
- 26 Jenkins, A. (Apr, 2021). ‘14 Top inventory management trends to know in 2021’. Retrieved from Netsuite.
- 27 (Apr, 2021). ‘3 Ways artificial intelligence/AI can help with supply chain digital transformation’. Retrieved from SupplyChain247.
- 28 Bokhan, K. (Nov, 2020). ‘Machine learning in supply chain: 8 use cases that will impress you’. Retrieved from N-iX.
- 29 (Jul, 2020). ‘8 Ways AI can improve inventory management’. Retrieved from Matellio.
- 30 Stringfellow, A. (Feb, 2022). ‘How to reduce logistics costs: 19 Experts reveal ways organizations can cut their logistics transportation and carry costs’. Retrieved from Camcode.