Blockchain Regulation and Smart Contracts
One of the most debated technology trends in the past few years, blockchain has disrupted a broad cross-section of industries and businesses, from banking and financial services to insurance, healthcare, and information technology.
Its continued adoption has made business leaders and professionals recognize blockchain’s move from a relatively unknown, seemingly daunting innovation to a technology that many global corporations now rely on. This is what you need to know:
Blockchain explained
A distributed database that is shared digitally, a blockchain is essentially a ledger or a record of transactions that cannot be changed, deleted, or destroyed. Data is stored in individual blocks via cryptography, making blockchain a remarkably safe, transparent way of storing information.
A blockchain network can be used to digitally track and trade just about anything, at a reduced cost and with lowered risk. The technology helps decrease an individual’s reliance on third-party and intermediary service providers, such as banks.1
Six benefits of blockchain
Introducing blockchain as an innovative method of delivering peer-to-peer information has many benefits. These include:
1. Increased financial inclusivity
Blockchain enables financial institutions to create greater coherence throughout their ecosystem, extend their knowledge of their customers, detect fraudulent transactions more successfully, and mitigate against risk more effectively.2
2. Decreased centralized power
Rather than being stored centrally, each block is copied and distributed around an entire peer network. Each time anyone within this network adds a new block to the chain, this is added to everyone’s copy simultaneously.3
3. Enhanced security
In contrast to traditional banking, payments and money transfers made via blockchain are faster and easier to trace. Blockchain’s cryptographic algorithms bring a new level of security.4
4. Reduced costs
Because blockchain creates efficiency in processing transactions, it lowers an organization’s costs. This agility is carried across to a reduction in manual tasks, including aggregating and amending data, and facilitating the reporting and auditing processes.5
5. Greater transparency
As blockchain uses a distributed ledger, transactions and data are recorded in multiple locations. Everyone with access can view the same information at the same time, providing full transparency and eliminating fraud.6
Blockchain’s potential risks
Although the technology offers a number of benefits, it can contain risks, which can be classified into these four broad categories:7
1. A robust network is critical
To reap the full benefit of blockchain, you’ll require a sturdy network of users with a wide distribution of nodes (these verify each batch of network transactions: the ‘blocks’).
2. Expensive and slow computation
In order to maintain consensus across the blockchain, every node runs the blockchain. This is a time- and energy-consuming process, as each node has to repeat a task to reach consensus.
3. Human error
If a blockchain is used as a database, the information captured in the database must be of a high quality and recorded accurately. It’s critical that quality assurance is prioritized.
4. Slow transactions
The slower transaction time makes it an unlikely competitor in the space of real-time transactions, or POS (point-of-sale) applications.8
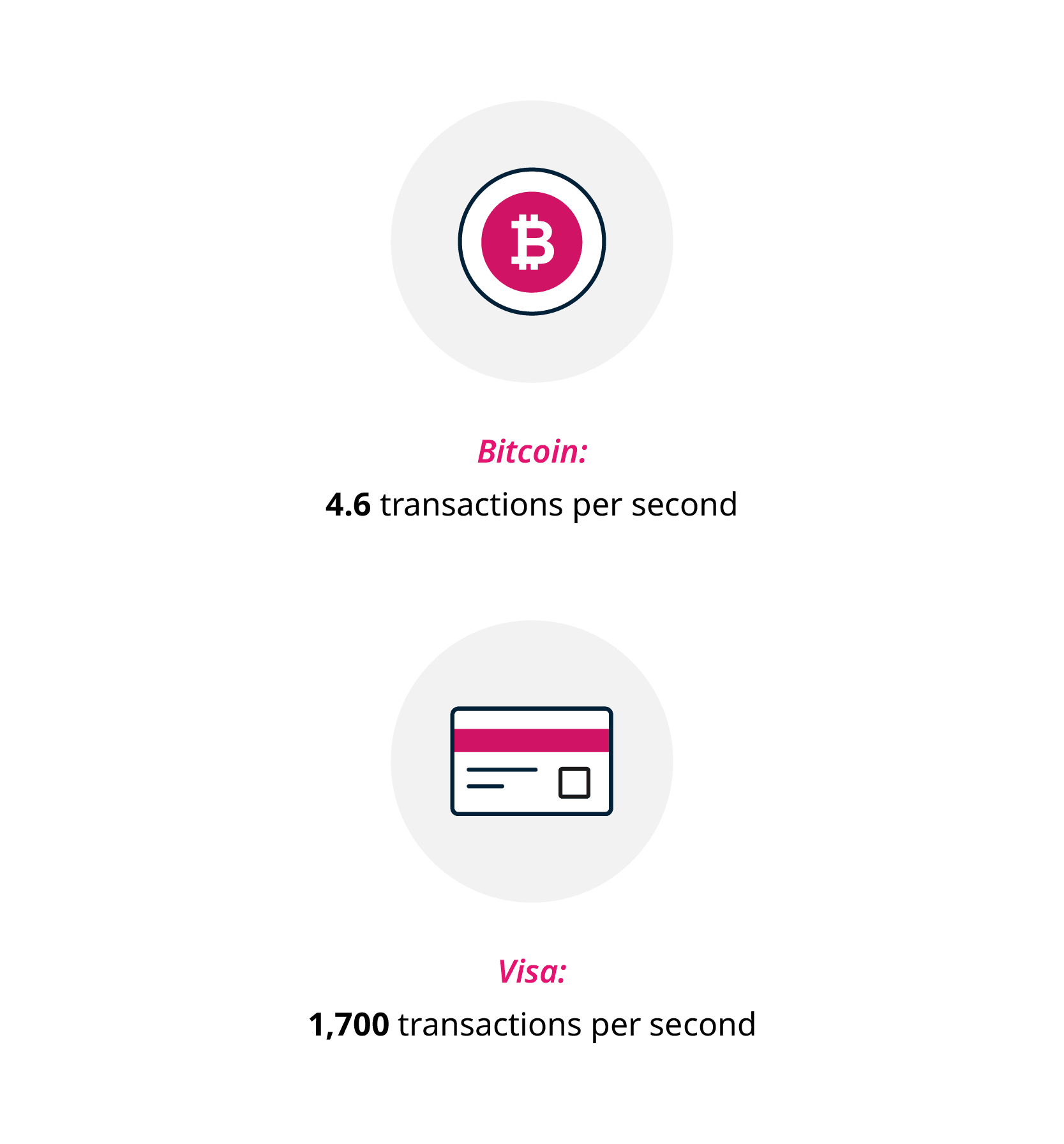
Because of blockchain’s decentralized nature, the need for regulation becomes a significant driver, which is often realized through smart contracts.
What is a smart contract?
Stored on a blockchain, this digital contract automatically performs a function when certain terms are met. A smart contract works in the following way:9
- A contract between two parties is coded into the blockchain.
- The contract will execute a task or action based on the coded terms that have been established.
- The digital asset is transferred automatically and the transaction is undisputed.
- If the transactional activity needs to be reviewed, regulators have access to the blockchain.
Smart contract transactions are recorded securely within the blockchain and are protected from changes. Such protection establishes trust in the process and the information.
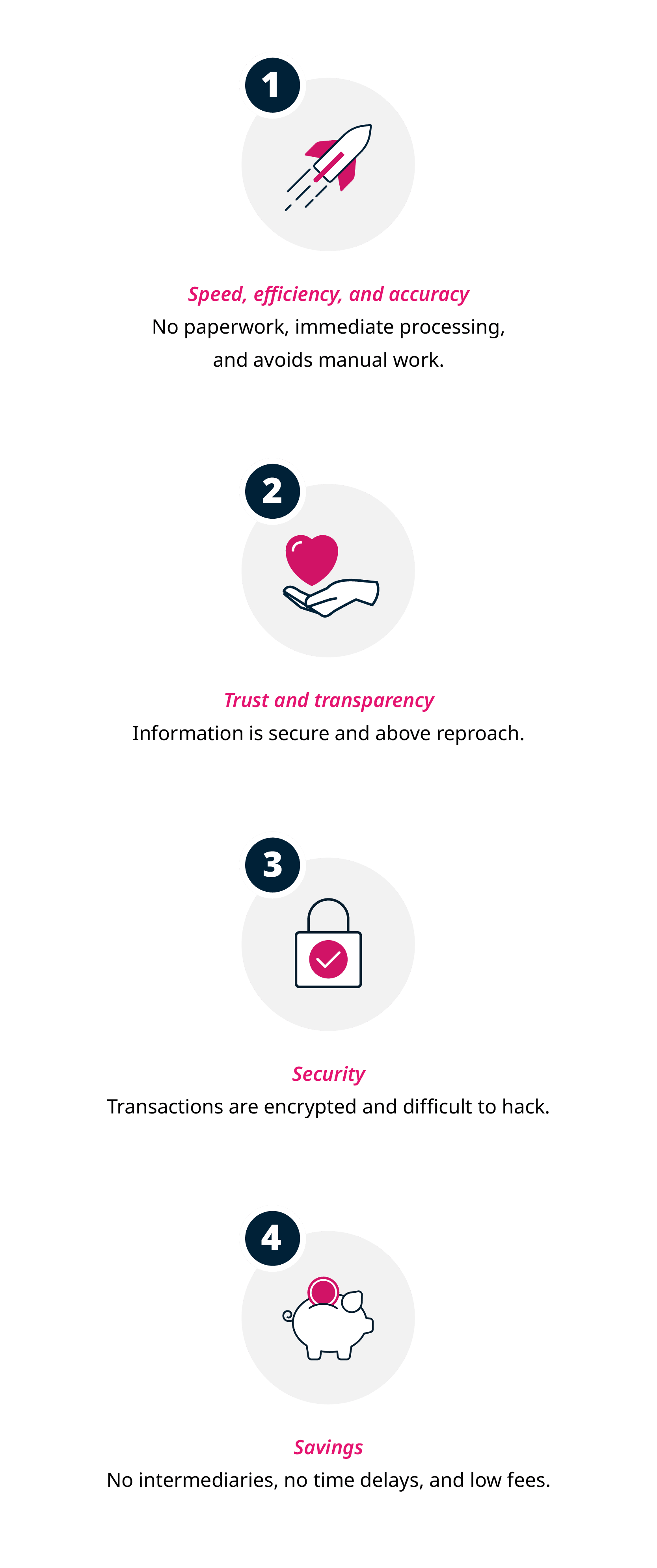
Four key reasons for using smart contracts
The primary benefits of blockchain are reflected in the reasons for utilizing smart contracts. A blockchain smart contract ensures:10
Smart contracts and blockchain in law
It’s now possible for firms to integrate blockchain technology within their practices. OpenLaw, a blockchain-based protocol for the creation and execution of legal agreements, is the first project to enable the creation of smart legal forms. Using OpenLaw, lawyers can efficiently engage in transactional work, and digitally sign and store legal agreements in a secure manner – leveraging blockchain-based smart contracts.11
Other legal use cases include:12
- Property
The real estate sector has multiple intermediaries. Blockchain can help the property owner bypass intermediaries and register their property on a public ledger. Sales are also transparent, with minimal transactional costs.
- Intellectual property rights
Blockchain offers a secure and efficient way of storing and proving patents, copyrights, and trademarks. Moreover, smart contracts leverage non-fungible tokens, also known as NFTs, which use cryptographic tokens to indicate ownership.
As blockchain regulation and technology matures, we’ll see it impacting and disrupting many different industries, organizations, and careers. It’s important to understand how blockchain functions, the ecosystem within which it lives, the regulations that surround it, and how it can be incorporated into your business.
Enhance your knowledge and skills on the Blockchain and Digital Currency: The Future of Money online short course from the University of Cape Town (UCT). In six weeks, you’ll learn how blockchain works and operates within the current and future financial system. Watch the course trailer to find out more.
Gain insight into the potential of crypto assets and blockchain technology
- 1 Conway, L. (Nov, 2021). ‘Blockchain explained’. Retrieved from Investopedia.
- 2 (Nd). ‘Inclusion through distribution. How blockchain supports financial inclusion’. Retrieved from Deloitte China. Accessed November 24, 2021.
- 3 Rejeb, A., et al. (Jan, 2021). ‘Centralized vs. decentralized ledgers in the money supply process: A SWOT Analysis’. Retrieved from AIMS Press.
- 4 Likos, P. (Sep, 2021). ‘How blockchain can transform the financial services industry’. Retrieved from US News.
- 5 Pratt, M. (Jun, 2021). ‘Top 10 benefits of blockchain technology for business’. Retrieved from TechTarget.
- 6 (Nd). ‘Benefits of blockchain’. Retrieved from IBM. Accessed November 24, 2021.
- 7 (Jun, 2021). ‘Disadvantages of blockchain’. Retrieved from Day One Tech.
- 8 K, L. (Jan, 2019). ‘The blockchain scalability problem and the race for Visa-like transaction speed’. Retrieved from Towards Data Science.
- 9 (Nd). ‘What are smart contracts on blockchain?’. Retrieved from IBM. Accessed November 24, 2021.
- 10 (Nd). ‘What are smart contracts on blockchain?’. Retrieved from IBM. Accessed November 24, 2021.
- 11 (Nd). ‘Real world contracts from Ethereum’. Retrieved from OpenLaw. Accessed November 25, 2021
- 12 Malik, P. (Mar, 2021). ‘What are smart contracts? +Benefits, limitations, use cases’. Retrieved from WhatFix.
