How To Become A Cybersecurity Analyst
Protecting the security and integrity of data is vital for businesses and organisations, as sensitive data leaks can cost companies millions in lost revenue or ransom demands. The Equifax hack of September 2017 cost the company US$4 billion in market value in under a week, and that doesn’t include the costs related to responding to the crisis and cleaning up the mess Equifax faces.

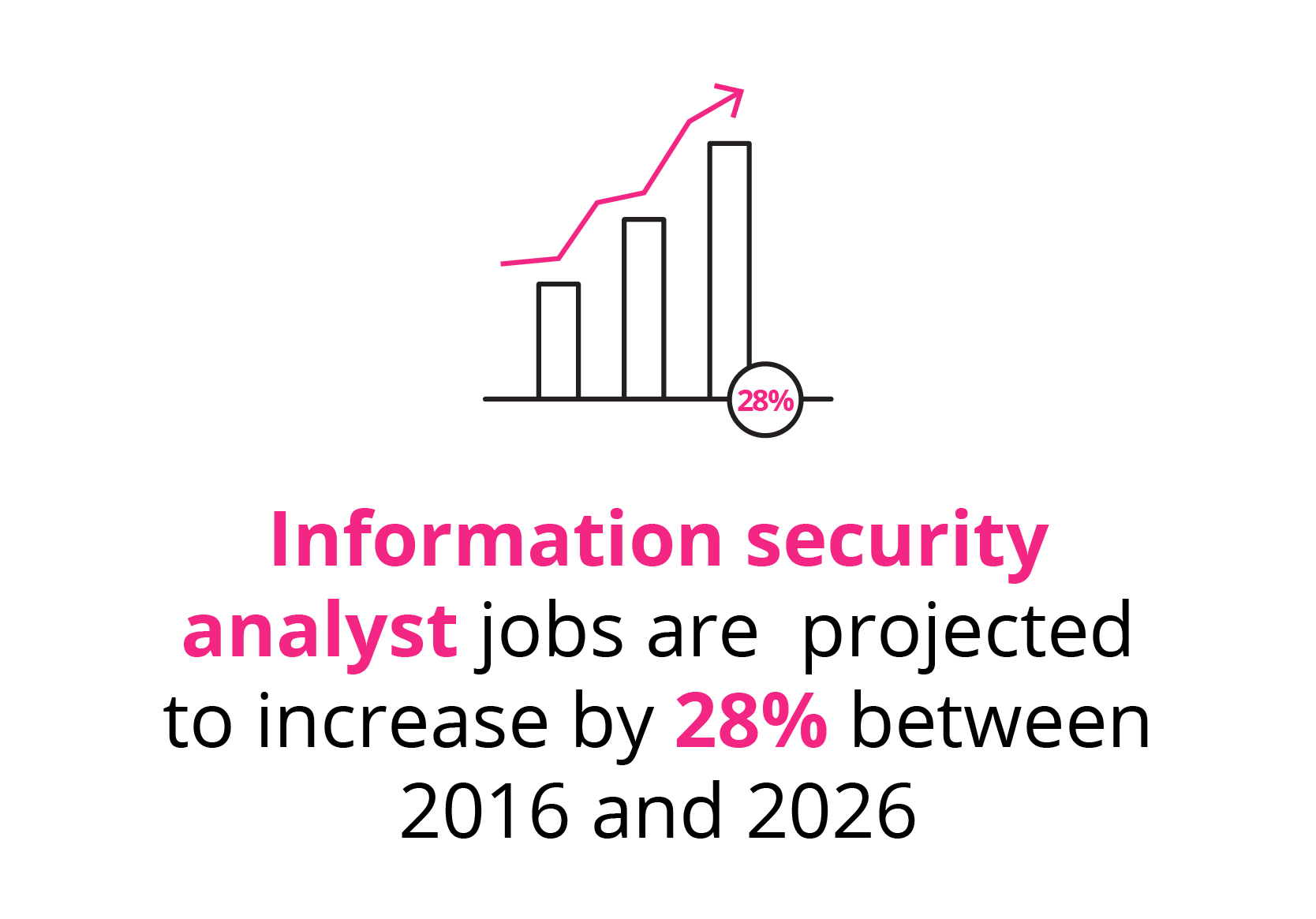
With devastating cyberattacks on the rise and businesses becoming more aware of the costs associated with them, demand for qualified cybersecurity analysts is surging. According to the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS), information security analyst jobs are projected to increase by 28% between 2016 and 2026, much faster than the average for all occupations during that decade.
What are the key responsibilities of a Cybersecurity Analyst?
Cybersecurity Analysts are expected to maintain their organisation’s cybersecurity defense systems, helping to keep the company’s infrastructure and sensitive data safe from hackers or cyberattackers. They need to work closely with the organisation’s Chief Technology Officer and use their knowledge of computers, hardware and software to monitor and analyse data from various security systems.
An effective cybersecurity analyst needs to be able to clearly and quickly communicate security information to fellow analysts and customers, and put their technical skills to use in order to respond to threats and emergency security incidents in a timely manner. They also need to constantly develop and improve cybersecurity countermeasures in place to prevent malicious activity.
Other key responsibilities of a Cybersecurity Analyst include making an impact in the following three areas:
Cybersecurity |
|
Information Systems Management |
|
Information Technology Management |
|
Cybersecurity |
|
Information Systems Management |
|
Information Technology Management |
|
Related Content: How To Detect A Cyberattack
What is the career path of a Cybersecurity Analyst?
Given the importance of cybersecurity defenses to any and every organisation, job opportunities can be found across sectors and industries, from healthcare to financial services and insurance to education. Cybersecurity Analysts have also been in high demand in military and government agencies. For example, the US Department of Defense announced plans in 2015 to hire up to 3,000 cyber-savvy civilians to be part of the US Cyber Command.

Cybersecurity Analysts generally need to have previous experience in a related occupation, such as in roles in an organisation’s information technology department, often as a IT Managers or IS Managers. No matter their professional history, Cybersecurity Analysts should have skills in:
- Cybersecurity management
- Information technology management
- Information systems management
- Internet of things integration (IoT)
- Artificial intelligence (AI)
- Data analysis
What is the potential salary for a Cybersecurity Analyst?
A Cybersecurity Analyst’s salary depends on the type and size of the organisation they work for. If the data and systems you’re responsible for looking after include highly-sensitive information pertaining to global issues, such as working for governmental agency, you can expect pay that relates directly to your level of responsibility.
Other than experience in the field and place of employ, the skills that increase pay for this job the most are:
- Security testing and auditing
- Computer security
- Security policies and procedures
- Security intrusion detection
Click on a country to see what you can expect to get paid as a Cybersecurity Analyst in either South Africa, the United Kingdom or the United States of America:
What are the education and training requirements for a Cybersecurity Analyst?
A typical minimum qualification for aspiring Cybersecurity Analysts, required by most employers, is a bachelor’s degree in computer science, programming, or similar fields. Some organisations may also want applicants with advanced training, industry certifications or work experience in a related field such as information technology.
Few firms prefer candidates to have an advanced degree, such as a Master of Science in Information Assurance and Cybersecurity, which may be hard to come by as the field of expertise is still in its early stages.
If you’re currently working in an IT or IS position, prospective employers may offer tuition assistance to help employees attain a degree or professional credentials in order to move into the role of Cybersecurity Analyst. Due to the extremely sensitive nature of the data Cybersecurity Analysts are tasked with protecting, those seeking to move into cybersecurity positions with military or government agencies are often required to undergo background checks, and obtain security clearances and industry certifications.
Which skills do you need next?
Download a course prospectus to find out how one of these online short courses can help you become an Cybersecurity Analyst.






